Analysis of Mooring Bollard Failures: How to Prevent
Mooring bollards are used to secure barges, ships and other vessels at docks, piers, or berths. The bollards are subjected to the full force of the vessel’s mooring operation, and environmental loads like wind, waves and tidal movement. Despite their robust design, bollard failures can occur. They can cause costly damage, create environmental hazards and, most importantly, pose safety risks. This article focuses on a detailed analysis of the causes for mooring bollard failures and effective measures that can be taken to prevent mooring bollard failures, improving the safety and reliability of marine mooring bollards.

Table of Contents
Understanding the Function of Mooring Bollards
A mooring post is a cylindrical heavy-duty post, usually made of steel or concrete. It’s strategically placed along the dock or quay to secure the mooring line for vessels. The purpose of the mooring bollard is to act as a solid point to which the cables or ropes used to tether a vessel can be attached. It also absorbs the dynamic forces exerted on the vessel while it stays in the port. The bollards must be able to withstand both dynamic and static forces. These can be significant depending on the size of the vessel, environmental conditions and loading operations.
The design of the marine mooring bollard must take into account:
- The Size and Type of Vessel: larger vessels, such as oil tankers, container ships and cruise ships, require stronger bollards.
- Environment Forces : Wind, waves and tides can all affect the stability of vessels moored.
- Operational Dynamic: Bollards can be subjected to extreme stress during docking and undocking and adverse weather conditions.

Causes of Mooring Bollard Failures
Understanding the causes of mooring bollard failures is crucial for improving safety and operational efficiency in marine environments, as well as minimizing risk.
1. Design Flaws
A flaw in the engineering or design of the mooring bollard is one of the most common causes of failure. In order to design a bollard, it is necessary to take into account several factors, such as the type and size of the vessel, the forces that are exerted when mooring and the environmental conditions, like wind, waves and tides. Bollards which are not designed properly or do not meet the required strength requirements can fail under stress.
Underestimating the maximum weight that a bollard can experience when docking or during extreme weather conditions can be a major problem. The bollard may collapse under pressure if it is not designed to withstand the force of large vessels or sudden changes in the environment. Poorly reinforced structures such as weak seams or inadequate welds can also compromise the integrity of the bollard, causing it to fail.
2. Material Degradation and Corrosion
Material degradation can be significant when mooring bollards come into contact with harsh marine environments. Saltwater, humidity and temperature fluctuations are all factors that contribute to material degradation. The corrosion of steel and iron bollards is one of the main causes of failure. When the material reacts to oxygen and water, it weakens the structure. Unchecked corrosion can lead to cracks, pitting and loss of strength in the material, which ultimately leads to structural failure.
Even bollards constructed from materials that are more resistant to corrosion, like stainless steel, or composite materials, can be subjected to degradation. In a moist environment, galvanic corrosion may occur when metals come into contact. This can lead to an accelerated degradation. The fatigue caused by repeated loading and unloading can also cause materials to weaken, particularly in ports with high traffic where bollards are constantly stressed.

3. Installation Errors
Incorrect installation is another major cause of bollard failure. To function properly, a bollard must be anchored securely to the dock or quay in order to prevent any movement or displacement. When the bollard is subjected stress, it may shift or be dislodged if the foundations are not properly installed. Incorrect alignment or insufficient anchorage can cause installation errors that compromise the bollard’s ability to resist the forces during mooring.
A bollard that is not properly placed on the dock can be exposed to excessive stress due to heavy traffic or poor environmental conditions. Bollards placed in areas of high tidal force or heavy vessel traffic may fail if they are not strategically positioned.
4. Neglected Maintenance and Inspection
It is important to maintain and inspect mooring bollards regularly in order to ensure that they continue performing at their best. Wear and tear may go unnoticed and small problems can become major ones without routine inspections. Bollards that fail due to failure can be caused by failing to remove surface corrosion or inspect structural integrity.
Over time, corrosion and rust can build up, especially in lower portions of bollards exposed to water or harsh weather. Bollards can be weakened by cracks caused by previous wear and tear, fatigue due to repeated moorings, or abrasions from cables or ropes. Inspection and maintenance are necessary to address these signs. Otherwise, the bollard could fail when under load.
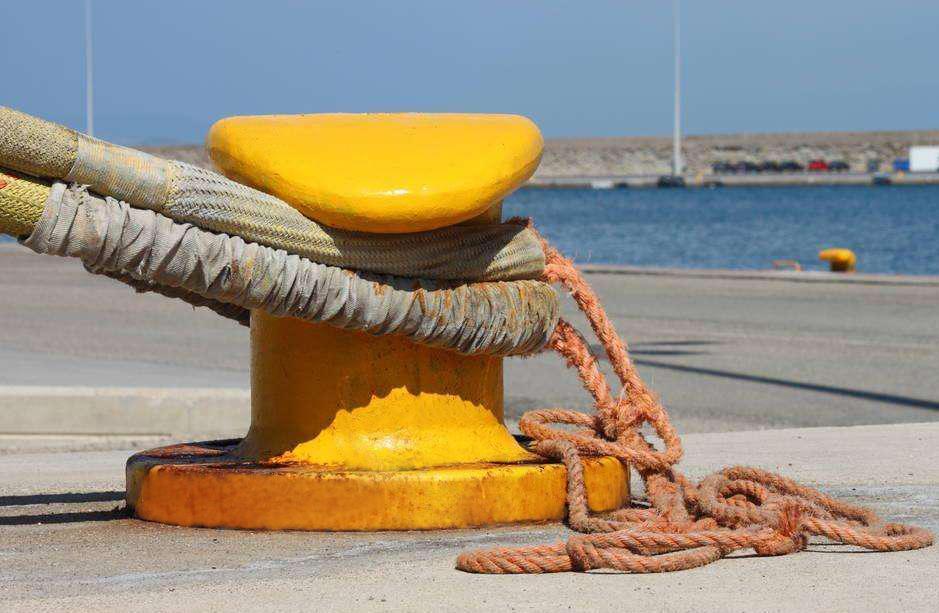

5. Excessive Loading and Overuse
The marine mooring bollards are designed to withstand a specific load, but can break if they are subjected excessive force. A bollard can be overloaded if it is used in excess of its capacity. This could happen if the vessel is large and heavy or if multiple vessels are moored at the same bollard.
Unreliable load calculations, incorrect docking techniques or vessel related issues can result in excessive loading. A vessel that is larger than expected or one that has been improperly moored may place greater stress on the bollard. When mooring ropes are not tensioned properly or when multiple lines are attached, the forces are concentrated. This can exceed the structural capacity of the bollard.
6. Environmental Factors
Marine environments present a variety of challenges to mooring bollards. Extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes or storms can place enormous stress on moored boats and their bollards. These conditions can increase dynamic forces on the bollard and cause failure if it is not designed to withstand these stresses.
The marine bollards are also subjected to additional pressure from waves and tides. The combined forces can exceed the capacity of the bollard if it is placed in an area that experiences strong currents and large waves. The stability of bollards can be affected by seismic activity, particularly if the structures are not designed to resist such forces.
7. Human Error and Operational Failures
Human error can contribute to bollards failing. While material or design problems are usually the cause of bollard failure, they may also be the result of human error. Improper mooring methods, such as incorrect rope tension or miscommunications between dock and vessel crew can cause excessive stress to the bollard. In addition, failing to adhere to established safety protocols and improper mooring management can increase bollard failure risk.
Poor coordination can lead to uneven loads on the bollard when multiple vessels are moored together. This can cause the bollard to be stressed beyond its capacity. If the vessel shifts or moves during docking and undocking this could also lead to unexpected loads on the bollard.

The Consequences Of Mooring Bollard Failure
| Consequence | Description |
| Damage to vessels | A bollard that fails can cause a vessel to drift or shift. This could lead to collisions with other vessels, dock structures or port equipment. |
| Operational Disruptions | Bollard failures can cause docking operations to be halted, resulting in delays in loading/unloading, and other port activities. This leads to financial losses, and inefficiency in the operation. |
| Safety Hazards | If a failure of the bollards causes the vessel to become loose or collide with structures, workers, crew members and individuals nearby are at risk for injury or death. |
| Environmental Impact | A drifting ship can cause oil spills or cargo losses. This may lead to environmental damage that will last for years and expensive clean-up operations. |
| Damage to Port Infrastructure | Bollard failures can cause damage to port infrastructure such as docks and piers. This will require expensive repairs. |
| Legal and Financial Liability | If you fail to comply, you may be subjected to legal action, fines and insurance claims. This can have a significant financial impact on port operators and vessel owners. |
| Reputation Damage | Failures of bollards on a regular basis can damage the reputation of a port facility, and lead to loss of business from clients, especially those who demand high reliability. |
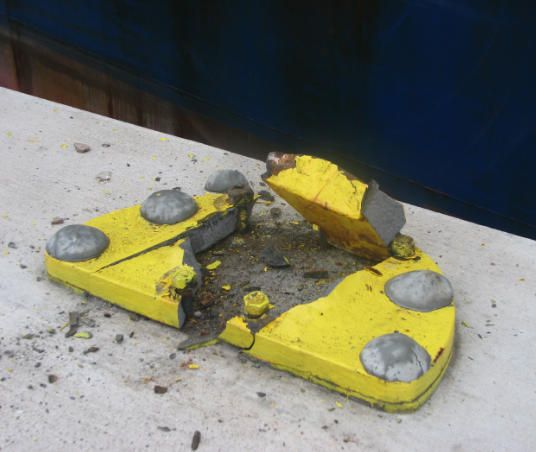

Key Strategies for Preventing the Failure of Mooring Bollards
1. Proper Design and Load Calculation
To prevent bollard failure, it is important to ensure that the bollard has been designed properly to handle the loads they will face in service. It is important to perform accurate load calculations in the design phase. This includes not only the size and weight of the vessels that will be arriving at the port, but also their dynamic forces. Included in this are the forces created by wind, waves and tides as well as the movement of the vessel during docking and undocking.
Mooring bollards need to be designed so that they can handle the maximum load anticipated. This often means considering the worst possible conditions. A bollard, for example, should be strong enough so that it can withstand the forces created by the biggest vessels in the port. These could be oil tankers or container ships. The design should also take into account environmental factors, such as high winds or storm surges. If bollards cannot withstand the forces they will face, they can fail, causing costly damage and safety hazards.
2. Use of High-quality, Corrosion-resistant Materials
Materials can be rapidly degraded by harsh marine environments where humidity, saltwater and fluctuating temperature can cause degradation. Steel is the most common material for bollards, but steel is prone to corrosion if exposed to seawater. Bollards that are corroded lose their structural integrity and can fail under moderate loads. It is important to use high-quality materials that are corrosion-resistant when making bollards.
This chart highlights the most common corrosion-resistant materials that are used to construct mooring bollards, including their advantages and typical applications. Each material has different durability and protection depending on the environmental conditions it is exposed to.
| Material | Description | Benefits | Common Applications |
| Stainless Steel | A steel alloy containing chromium that provides corrosion resistance. | Long lifespan, low maintenance and high structural integrity. | Ports with high traffic, coastal areas and industrial docks. |
| Galvanized Steel | The zinc layer on steel is designed to prevent corrosion. | Highly resistant to corrosion and economical, even in marine environments. | Smaller ports and low-cost applications. |
| Aluminium | The corrosion resistance of this lightweight metal is well known. | Lightweight, with a good aesthetic appearance, and excellent resistance to corrosion caused by saltwater. | Light-duty docks for recreational use. |
| Composite Materials (Fiberglass-based or Resin Based) | Materials consisting of a mixture of fibers (glass or carbon) and resin to create a structure that is non-metallic and corrosion resistant. | Lightweight, durable and easy to maintain, this product is resistant to seawater. | Ports that are subject to extreme corrosion, such as those used offshore. |
| Bronze | A corrosion-resistant alloy made primarily of copper and tin. | Natural corrosion resistance makes this material strong and durable in marine environments. | Used historically for marine equipment and specialized mooring application. |
| Alloys of Copper and Nickel | Alloys containing copper and nickel are known for their excellent resistance to corrosion in seawater. | Specially in saltwater environments, this product has an exceptional resistance to corrosion and biofouling. | Offshore platforms and marine environments that pose a high biofouling threat. |
| Thermoplastic Polymers | Bollards are constructed from high-performance plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene. | Lightweight, flexible, and resistant to corrosion. | Ports and harbors with less heavy-duty docking requirements. |
Anti-corrosion coatings are recommended in addition to durable materials. The application of protective coatings such as polyurethane or epoxy on a regular basis helps protect the surface of the bollard from the corrosive effects of seawater. This extends its life and prevents premature failure.
3. Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Routine inspections and maintenance are the best ways to avoid mooring bollard failure. Even the strongest of bollards will wear out over time. The structure of the bollard can be weakened by corrosion, cracks and fatigue caused by repeated loading. It is important to conduct regular inspections in order to identify these problems early, before they cause catastrophic failure.
Bollards need to be checked regularly for signs of corrosion, rust and physical damage. Marine inspectors who are trained to assess bollard integrity can look for signs of damage, such as fissures or pitting. Ultrasonic testing and other non-destructive techniques (NDT) can be used to assess the internal structure of a bollard.
Marine mooring bollards also require periodic maintenance in addition to visual checks. Cleaning the surface of salt and debris is important, as well as applying new anti-corrosion coats and repairing any damage found during inspections. It is important to replace bollards with significant wear and damage in order to maintain the safety of the ports, as well as ensure that the vessels are moored securely.

4. Reinforced Installation and Strategic Placement
Installation of mooring bollards is as important as the design and quality of their materials. The installation of a bollard is crucial. Even the best designed bollard can fail if not done correctly. The bollard will not be able to resist the force of mooring lines if it is not installed correctly.
It is important to use the correct foundations and reinforce the dock structure when installing bollards. When bollards have been installed incorrectly, they are more likely than not to move or become loose under load. This can cause the vessel to be untethered, causing serious damage.
It is important to place bollards strategically. Bollards are best placed in areas where they will be less affected by excessive forces. This includes areas near areas of high traffic or strong tide currents. Placement of bollards where they will be under an uneven load, or subjected unnecessarily to stress, increases the chance of failure. Bollards must be evenly spaced and placed to avoid external forces such as wind or waves.
5. Training and Operational Protocols
If the correct operational procedures aren’t followed, even with the best materials, design, and maintenance, bollards can fail. It is important to train port staff and mooring teams in order to ensure that the bollards can be used safely and efficiently. Personnel must be trained on proper mooring methods, such as the tensioning of ropes correctly and the securing of vessels with the right number of mooring lines.
A bollard should not be subjected to excessive loads. This is an important aspect of safety. By using too tight ropes or by attaching too many lines, you can overload bollards and cause them to fail. Port operators can reduce the risks of bollard failures due to human errors or negligence by establishing protocols for safe mooring.
Port operators can also adjust their mooring procedures in response to changing conditions by using real-time monitoring systems. If high winds or storms are forecast, the vessels can be moved into more secure mooring spots, and extra measures can be taken in order to reduce stress on bollards.

Summary
The analysis of the mooring bollard failures highlights the importance of a strong design, quality materials, correct installation, and routine maintenance. Port operators can reduce risks and improve safety for workers and vessels by addressing the causes behind bollard failure. In order to extend the life of mooring bollards, it is important to take proactive measures, which include improving design standards, ensuring the use of corrosion-resistant materials and proper maintenance.