How to Install Mooring Bollards Effectively in Harsh Environments
Installing marine mooring bollards for mooring in extreme conditions is an essential engineering job that guarantees the secure mooring of vessels even in extreme conditions, such as high winds, seawater that is corrosive as well as ice and unstable soils. These structures should be strong as well as corrosion-resistant and solidly anchored to stand up to the environmental stresses and operational loads. This article will focus on installing mooring bollards into difficult conditions. This article provides a step-by-step guide to installing mooring bollards in difficult environments.
What are Mooring Bollards
Mooring bollards can be sturdy fixed posts that are placed on wharves and docks or quaysides in order to ensure the mooring lines of a ship are secured. They function as crucial anchoring points to keep vessels safe as they dock. They are typically made of cast iron, ductile iron or stainless steel, bollards designed for mooring are built to withstand the rigors of heavy load, tough sea conditions, and continuous usage. The shapes and sizes of these bollards differ based on the type of vessel and mooring requirements. They provide safe and secure berthing even in demanding conditions.

A Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Mooring Bollards Effectively in Harsh Environments
1. Site Assessment and Environmental Evaluation
Before the installation process begins, you must complete a thorough survey of the site to evaluate the geotechnical and environmental conditions.
- Assess the tidal range and the wave action and the strength of the current.
- Check soil properties to determine stability, capacity for bearing, and the possibility of erosion.
- Examine environmental stressors like the impact of ice, seismic activity as well as salt spray.
This helps to determine the best bollard type, foundation design, and the protective measures that are required.
2. Selecting the Right Mooring Bollard
Selecting the appropriate bollard type and material is crucial to ensure long-term durability.
This is a concise and clear chart that lists the different kinds and materials used in bollards for mooring, as well as their most common applications and features:
| Type of Bollard | Common Materials | Typical Applications | Material Characteristics |
| T-Head Bollard | Cast Steel, Ductile Iron | General-purpose ports, commercial docks | High strength, suited for heavy loads |
| Horn Bollard | Cast Steel, Stainless Steel | Tidal zones, multi-angle mooring | Allows multiple mooring line angles |
| Single Bitt Bollard | Cast Iron, Cast Steel | Small vessels in waterways and rivers | Small design, easy line handling |
| Double Bitt Bollard | Ductile Iron, Stainless Steel | Shipyards ferry terminals, shipyards | Allows multiple lines, with strong anchorage |
| Kidney-shaped Bollard | Cast Steel, Galvanized Steel | Container terminals, areas of high-traffic | Optimized for applications that require high load. |
| Cleat Bollard | Stainless Steel, Aluminum | Yachts, marinas, small docks | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant |
| Pillar Bollard | Cast Steel, Composite Materials | Industries ports, areas with space limitations | Vertical profile is ideal for installations with tight spaces |

3. Foundation Engineering and Site Preparation
The bollard’s effectiveness is as solid as its foundation. In coastal or soils that are unstable, zones, engineers could require deep foundations made of driven piles or reinforced concrete blocks and rock anchors. The foundation should be able of spreading forces of mooring evenly even in extreme pressures from ice or tidal.
Construction teams typically have to establish dry working conditions by using cofferdams, dewatering systems or the use of tidal scheduling. In colder regions, thermal blankets and concrete additives are used to avoid freezing while curing.
4. The Process of Installing the Bollard
Follow the exact installation procedure for ensuring proper operation
- Anchor bolts are placed on the foundation template in accordance with the layout engineered by engineers.
- Pour concrete reinforced and give sufficient time for curing. In colder climates, apply heater blankets and admixtures to ensure the proper curing.
- Install the bollard onto the foundation that has been cured, aligning the bolt holes precisely.
- Secure anchor bolts according to specifications with calibrated tools.
- Cover the bolt recesses with sealant and apply protective coatings on exposed surfaces.
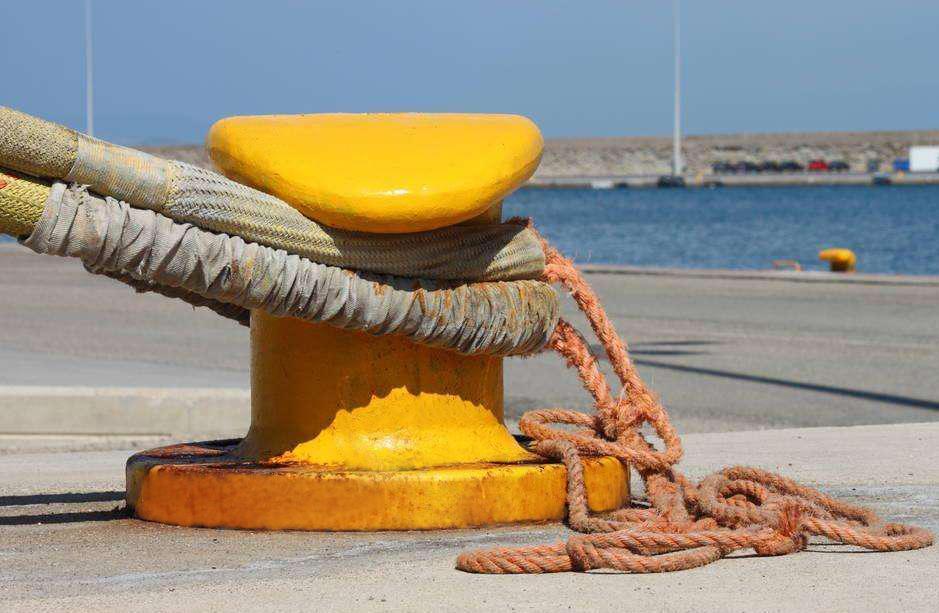

5. Implementing Corrosion and Ice Protection
To prolong the duration of mooring bollards extreme conditions:
- Apply corrosion-resistant coatings to bollards and anchors.
- Utilize cathodic protection systems (sacrificial anodes, or more the impressed current) in tidal and saline zones.
- Create a design that allows to load ice by selecting bollards that are reinforced or have smooth surfaces to minimize the buildup of ice.
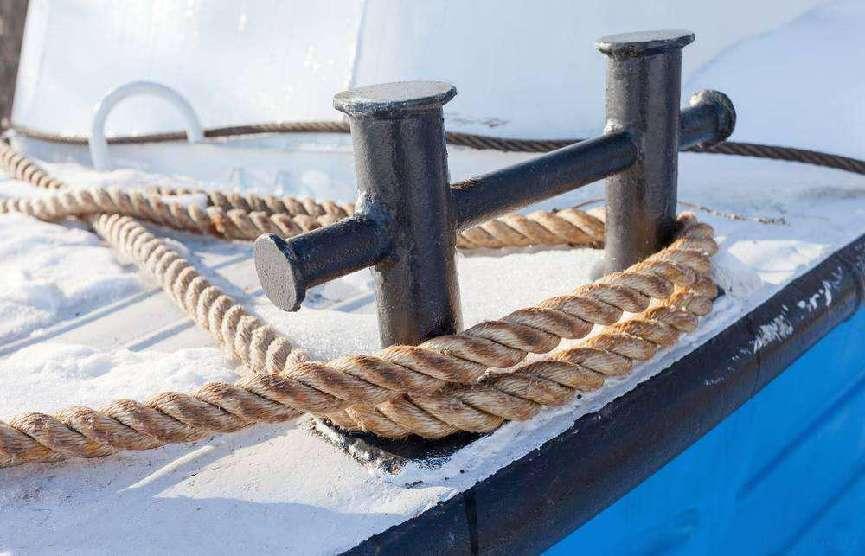

Testing and Quality Assurance after the installation of Mooring Bollards
| Stage | Test Type / Inspection | Purpose | Key Standards / Guidelines |
| 1. Material Verification | – Analysis of the chemical composition Mechanical property tests (tensile and hardness) | Verify that the bollard dimensions are in line with the design sketches | ASTM A27, ASTM A148, EN 1563 |
| 2. Dimensional Inspection | Check tolerance – Surface measurement of the finished surface | Verify that bollard dimensions are in line with the design sketches | ISO 2768, Manufacturer’s specifications |
| 3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) | – Ultrasonic Testing (UT) – Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) – Dye Penetrant Testing (PT) | Find flaws on the surface and internal like cracks or voids | ISO 9712, ASME V, EN 473 |
| 4. Load Testing | Static pull tests Test load for proof | Verify structural performance in simulation mooring loads | ISO 13795, PIANC Guidelines |
| 5. Coating Inspection | – Dry Film Thickness (DFT) Tests for adhesion – Visual inspection | Check that anti-corrosion coatings comply with performance standards | ISO 12944, NORSOK M-501 |
| 6. Bolt Torque Verification | Test of torque wrenches | Verify anchor bolts are tightened according to torque specifications. | Manufacturer’s torque specifications ISO 898 |
| 7. Final QA Documentation | Reports of inspections Test certificates for load. – Material traceability | Full traceability and conformity proof for port authorities | ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems |

Planning for Long-Term Maintenance of Mooring Bollards
The planning for maintenance over the long-term following the installation of mooring bollards is crucial to ensure their continual performance in terms of safety, durability, and security particularly in harsh environments. Regular maintenance can prevent problems, extends the lifespan of the bollard and lowers the overall cost of operation.
- Routine Visual Inspections
The first step to long-term maintenance is to conduct regular visual inspections. These should be done every month or after major weather-related events, like high winds or storms. The aim is to spot any signs of wear, damage or corrosion. A regular inspection of your bollard’s surfaces, anchor points, as well as the surrounding area will ensure that the early signs of trouble are discovered before they lead to more serious failures. Be aware of saltwater accumulation, ice formation and indications of growth in marine that can affect bollard’s integrity over time.
- Cleaning and Re-coating
Cleansing the bollards is vital for maintaining their corrosion resistance especially in places that are where they are exposed to saltwater as well as high humidity. A thorough cleaning must be performed every year to eliminate algae, salt as well as other aquatic life which may cause degrading. Following cleaning, the bollards must be coated with anti-corrosive finishes. This ensures their structural integrity and shields against the harsh environment of marine life. In environments that are particularly hostile periodic cleaning and re-coating could be required.
- Bolt Tightening and Torque Checks
With time the bolts holding the bollard to its foundation could become looser, affecting its ability to securely anchor the mooring lines. After-load or semi-annual inspections must include verification of bolt torque. This will ensure that the bolts are tightened in accordance with the specifications of the manufacturer. Extreme conditions like freezing temperatures, could affect the bolt’s tension, and it’s crucial to make sure whether bolts are securely secured to ensure bollard’s strength.
- Foundation and Structural Integrity
The foundation that supports the bollard plays an essential function in the stability of the mooring bollard. Every year, check the foundation for indications of settlement, erosion, or shifting. If you live in areas that have tidal fluctuations or heavy currents, or unstable soil conditions the foundation could need more frequent inspections. If you notice any issues like cracks or subsidence of the base, it must be addressed immediately to avoid bollard damage.

- Alignment and Functionality Checks
In time, mooring bollards could get misaligned because of the stress of heavy load moorings shifty ice, seismic activity. It is crucial to inspect the alignment of the bollard each six-month period to make sure that it’s working properly. Uneven alignment could result in unsafe mooring conditions, possibly putting vessels at risk or even workers. A correctly aligned bollard can ensure that mooring lines remain securely fixed and work in the way they were intended to.
- Documentation and Reporting
A crucial aspect of maintaining the bollard for a long time is keeping detailed documents of all inspections and tests repair, maintenance and inspection actions. The documentation is an evidence of the bollard’s condition throughout time and helps ensure the compliance with maritime laws. These records also allow you to determine recurring issues that might need to be addressed and form the basis for future planning.

Summary
Installing mooring bollards for mooring in extreme conditions requires a combination of high-end engineering, environmental consciousness and solid construction practices. If you follow the steps of evaluation of your site and material selection, to the proper anchoring and maintenance plans, you can ensure longevity of the safety and performance of the marine mooring bollard in the toughest conditions.