Rapid Deployment Mechanisms in Stockless Anchors
Stockless anchors are greatly adopted in commercial shipping, on naval vessels and on offshore platforms for the ease of use, ease of handling and the owning of high efficiency. As maritime work requires better safety levels, faster anchoring, and the rapid fostering of new mechanisms, the evolvement of rapid deployment mechanisms in stockless anchors is key. Such systems minimize operational time, enhance ships safety, and streamline stockless anchor retrieval processes.

Importance of Rapid Deployment for Stockless Anchors
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Stockless anchors are central to the passenger vessels and their position shifts. During a port maneuver, offshore operation, or an emergency drill, optimized stockless anchoring systems minimize the time spent on a particular action, thus greatly enhancing operational efficiency and workflow for shipping vessels and operations.
Ensuring Safety in Maritime Operations
In poor weather, storms, strong maritime currents, or a sudden need to turn on a dime; the ability to drop anchor can mean the difference between floating gently and smashing into a pier. Most ship collisions and groundings owe their occurrence to the sudden change in weather, and the quick response and rapid anchor deployment systems, to make their mark and minimize the collisions and possible damage.
Reducing Mechanical Stress and Wear
Lowering the anchor in a gentle, swift action greatly minimizes the wear on the chain, windlass and of course the primary anchoring mechanisms, thereby extending the longevity of all anchor devices significantly. It also minimizes the total maintenance costs which need to be put into the anchoring systems, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the ship.
Supporting Modern Automation Systems
Ships these days are defined by their automated control systems, making navigation and anchoring processes a walk in the park. These systems also incorporate rapid deployment mechanisms that allow for complex maneuvers to be executed remotely while minimizing the risk of error and human intervention.
Improving Emergency Response Capability
If there is ever a critical case of an engine malfunction or in the rare instance of a sudden weather change, the ability to rapidly release a stockless anchor can be a game changer in avoiding an accident by providing stability to the vessel and the crew on board. In this sense the free-fall and controlled variants of rapid deployment systems would be vital in providing an instant and necessary response.
Enhancing Overall Vessel Readiness
Relief systems, and most importantly rapid deployment mechanisms, are vital for a vessel to be operational and ready to provide crew members the ability to anchor regardless of circumstances. Such abilities are crucial for commercial and military operations, in addition to offshore operations, in a bid to guarantee that vessels can respond to their most critical operational demands.

Key Components of Rapid Deployment Mechanisms in Stockless Anchors
| Component | Function | Benefit |
| Windlass / Capstan | Provides torque to lift or lower the anchor chain | Enables controlled and rapid anchor deployment |
| Hydraulic Drives | Delivers high torque for heavy anchor handling | Allows fast, reliable deployment under load |
| Electric Motor Drives | Provides precise speed control and energy-efficient operation | Integrates with automated ship control systems |
| Hybrid Hydraulic-Electric Systems | Combines high torque with accurate control | Optimizes both speed and precision during deployment |
| Chain Stoppers | Holds the anchor securely once deployed | Prevents accidental chain overrun and ensures safety |
| Brakes | Controls the speed of anchor lowering | Prevents abrupt drops, reducing mechanical stress |
| Hawse Pipes | Guides the anchor from storage to water | Ensures smooth exit of the anchor, reducing friction and alignment issues |
| Guide Rollers | Supports the anchor as it passes through the hawse pipe | Minimizes friction and ensures rapid, smooth deployment |
| Chain Tension Control Systems | Monitors and adjusts tension during lowering | Maintains controlled descent, preventing jerks or sudden chain stress |
| Free-Fall Mechanisms | Allows immediate release of the anchor in emergencies | Provides the fastest possible deployment when rapid response is required |
| Automation and Monitoring Systems | Tracks anchor position, chain tension, and deployment speed | Reduces human error and enables remote-controlled, precise operations |
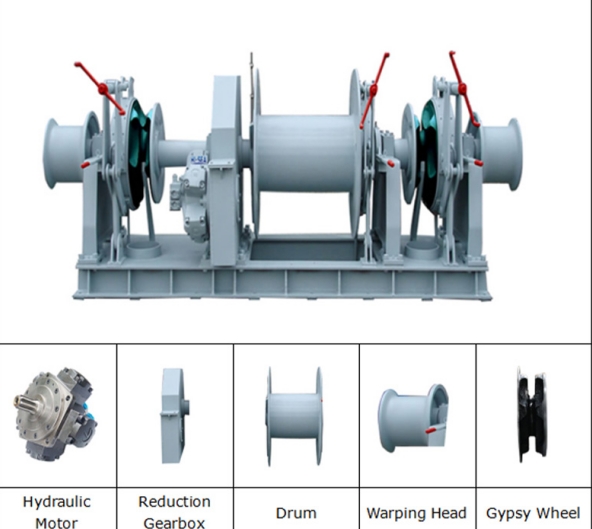
How Rapid Deployment Mechanisms in Stockless Anchors Work
1. Controlled Release via Windlass and Capstan
Seamless anchor deployment begins with the windlass or capstan. These devices are equipped with the power and torque needed to either lower or lift the anchor chain. Crew members are able to control the precise speed needed to lower the anchor slowly and gently to the sea floor while reducing any jolts to the ship. Marine windlasses drop anchors at optimal speeds during rapid deployment to achieve maximum control and speed.
2. Role of Hydraulic and Electric Drives
Hydraulic drive systems deliver high torque when heavy stockless anchors need to move rapidly. They work best when immediate deployment is needed under high load conditions. On the other hand, Electric drives provide precise speed control with the added benefits of power saving. Nowadays, some vessels utilize modern systems that are hybrids of the two, combining high-torque and precise control to provide fast and reliable anchor deployment.

3. Chain Tension Management
During rapid deployment, proper control of chain tension is critical to avoid jerks and drops. More recent stockless anchor systems utilize sensors and automated chains that control the anchor lowering speed. These systems make sure that there is no slack in the chain and take responsive-mechanical actions to lower the anchor.
4. Hawse Pipe and Guide System
The hawse pipe allows the anchor to move into the water by descending from the position it has been stored. The guide rollers on the hawse pipe diminish both friction and alignment problems, allowing for rapid and smooth movement of the anchor. This ensures that the anchor, even when it is being deployed rapidly, is able to slip away from the hull, thereby avoiding any damage to it.
5. Free-Fall Deployment Mechanisms
In emergencies, several stockless anchors have mechanisms for free falls, which allow the anchor to drop in free fall and almost instantaneously. This capability is crucial when a vessel has to come to a sudden stop due to fast-changing weather conditions, a mechanical problem, or other obstructions in the water. Controlled systems of free fall usually have damping elements which reduce the tension of the chain when the anchor is released to the sea floor.
6. Automation and Monitoring Systems
Modern rapid deployment systems in stockless anchors use a combination of real-time monitoring and automation to streamline the entire process. The bridge crew is able to control the anchor and observe the tension in the chain and the speed at which the anchor is being deployed. Automation improves the time to response, decreases the chances of human error, and allows for reliable, repeatable use of anchors in difficult conditions.

Key Factors Affecting Deployment Speed of Stockless Anchors
| Factor | Description | Impact on Deployment Speed |
| Anchor and Chain Weight | Heavier anchors and chains require more force to lower and control | Slows deployment unless machinery provides sufficient torque |
| Windlass and Drive Type | Type of drive system (hydraulic, electric, hybrid) and its torque capacity | Advanced drives enable faster, smoother deployment |
| Vessel Size and Bow Design | Hull geometry and bow clearance influence anchor path | Poor alignment or limited clearance can reduce deployment speed |
| Environmental Conditions | Wind, current, waves, and sea state | Strong currents or rough seas may require slower, controlled lowering |
| Chain Tension Control | Systems that monitor and adjust chain tension during lowering | Proper tension control prevents jerks and allows faster, safe deployment |
| Hawse Pipe and Guide Design | Friction, alignment, and smoothness of the path through the hawse pipe | Well-designed guides reduce resistance and speed up anchor exit |
| Maintenance and Lubrication | Condition of windlass, chain, brakes, and other components | Well-maintained systems operate more reliably and at higher speeds |
| Deployment Mode | Normal controlled lowering vs. free-fall release | Free-fall deployment provides the fastest anchor release in emergencies |
Innovations in Rapid Deployment Technology for Stockless Anchors
Improvements in rapid deployment technology of stockless anchors are integrating new innovations in traditional anchoring structures and systems. These new technological systems assist in minimizing mechanical stress and enhancing the safety of ship operations, since vassals are now able to deploy marine anchor more quickly and more efficiently.
1. Automation and Remote Monitoring
The more recent stockless anchor systems are equipped with automation and remote monitoring capabilities to a greater extent than in the past. Monitored parameters such as anchor position, chain tension, and deployment speed in real time, thereby enabling bridge crews to control anchor deployment. This mitigates manual errors, streamlines the anchor deployment process through automation, and grants greater maneuverability to deployment planning during the rapid changes in weather and navigation.
2. Advanced Chain Tension Control Systems
The development of intelligent monitoring systems has greatly improved the capabilities of chain tension control systems in the automation and remote monitoring of stress and environmental conditions. Such systems eliminate jerks or drops from the system, leading to rapid, smooth and safe anchor deployment in all rest sea states.
3. Free-Fall and Emergency Release Mechanisms
Current innovations in stockless anchors permit the anchors to be deployed free fall with near instantaneous response in periods of greatest emergencies. Contemporary stockless anchor designs integrate chain damping systems to moderate chain tension in response to contact to the seabed in Stephen soft sea bottom encounters, enabling prompt action to avoid damage in severe conditions.
4. Lightweight High-Strength Materials
Incorporating advanced materials like high-strength alloy steels and composite chains decreases the weight of the entire anchor and chain assembly. The decreased weight of components allows faster deployment, less strain on windlasses and winches, and enhanced operational efficiciency.
5. Hawse Pipe and Guide System Enhancements
Improvements of hawse pipe and the associated guide rollers lessen friction and other anchor deployment alignment imperfections. Optimized channels enable fast and reliable storage exit of anchors, while decreasing the lowering speed operational caps.
6. Predictive Maintenance and Diagnostics
Predictive maintenance technologies have begun to be integrated into modern rapid deployment systems. Systems like these enable the prediction of failures by constantly monitoring the wear and performance of the equipment, ensuring deployment mechanisms are always operational and negating delays and downtime.

Summary
Rapid deployment mechanisms in stockless anchors have become essential for maritime operations due to the need for speed and safety. Hydraulics, electric, and automation systems inline with mechanical systems have greatly minimized the time needed to operate on an anchor and have reduced the stress placed on mechanical systems. Incorporation of new designs, automation, and real time monitoring improves the level of reliability and safety during anchoring, which enhances the operational readiness of the vessel in various maritime operational regions.



